
SD card - init, read and write
8.6.2018
From now on in the text we have CS card input mapped to RC1 pin of the MCU. Set it to one as the card is not active yet. Next the text variable comes handy.
#define SD_CS LATCbits.LATC1
SD_CS=1;
BYTE s[50];
Initialisation
The card initialisation requires several steps. First we send several dummy bytes (should be at least 70 bits) while SD_CS is being kept high. The card communication mode then changes to SPI. The SD_CS pin may be set to zero now.
Now we issue the series of the commands to figure out the card type. In my case it is SDHC card and the following code should return number 3 in the type variable.
BYTE type;
for (BYTE i=0;i<20;i++)
{
spiWriteSD(0xFF);
}
SD_CS=0;
sendSerialString("\nsending CMD0\n");
while ((status=sendCommandSD(CMD0,0))!=0x01)
;
sprintf(s,"status=%d\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
sendSerialString("\nsending CMD8\n");
if ((status=sendCommandSD(CMD8,0x1AA)) & 0x04)
{
type=1;
}
else
{
unsigned long status2=0;
for (BYTE i=0;i<4;i++)
{
status2=((status2<<8)+spiReadSD());
}
sprintf(s,"status2=0x%lX\n",status2);
sendSerialString(s);
type=2;
}
sprintf(s,"status=%d\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
sprintf(s,"type=%d\n",type);
sendSerialString(s);
unsigned long arg=((type==2) ? 0x40000000 : 0);
sendSerialString("\nsending ACMD41\n");
int count=0;
while ((status=sendACommandSD(ACMD41,arg))!=0x00)
;
sprintf(s,"status=%d\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
if (type==2)
{
sendSerialString("\nsending CMD58\n");
sendCommandSD(CMD58,0);
if ((spiReadSD() & 0xC0)==0xC0)
type=3;
for (unsigned char i=0;i<3;i++)
spiReadSD();
sprintf(s,"type=%d\n",type);
sendSerialString(s);
}
In addition the card can be set to work with 512 bytes large sectors issuing command number 16. The SPI communication rate can be increased as well if needed.
sendSerialString("\nsending CMD16\n");
status=sendCommandSD(CMD16,0x200);
sprintf(s,"status=%d\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
SSP2CON1bits.SSPM=0b0000;
The output of the program after the initial phase looks like this:

Reading
We know that the card is logically divided into sectors of size 512 bytes. Each of the sectors is accessible by its ordinal number starting with zero. There are commands for writing/reading one single sector and commands to work with multiple successive sectors. In the text we will discuss the first case only.
To read the block issue the command number 17 with demanded sector number as its argument. The card replies with one byte of 0xFE value indicating that 512 bytes of the sector data will follow immediately. We will read these 512 bytes and 2 more that include CRC.
BYTE data[512];
void readBlockSD(unsigned long blocknum,BYTE *data)
{
if (sendCommandSD(CMD17,blocknum)!=0x00)
{
while (spiReadSD()!=0x00)
;
}
while (spiReadSD()!=0XFE)
;
for (int i=0;i<512;i++)
data[i]=spiReadSD();
spiReadSD();
spiReadSD();
}
Writing
Issue command number 24 with sector number. Next send one byte with 0xFE value followed by 512 data bytes. In the end send 2 CRC bytes that may be arbitrary value - I send 0xFFFF in the code below. The card then replies with one byte information about data processing. There are three possibilities. First data will be processed, second data will not be processed due to the CRC check error, third write error occurred. The byte with "OK" information has the form of 0bxxx00101 when 'x's are "do not care" bits. Now issue command number 13 with 0xFF as argument and wait until the card finishes data writing and returns 0xFF byte.
void writeBlockSD(unsigned long blocknum,BYTE *data)
{
if (sendCommandSD(CMD24,blocknum)!=0x00)
{
while (spiReadSD()!=0x00)
;
}
spiWriteSD(0xFE);
for (int i=0;i<512;i++)
spiWriteSD(data[i]);
spiWriteSD(0xFF);
spiWriteSD(0xFF);
status=spiReadSD();
sprintf(s,"status=%X\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
sendSerialString("\nsending CMD13\n");
status=sendCommandSD(CMD13,0xFF);
status=spiReadSD();
sprintf(s,"status=%X\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
while ((status=spiReadSD())!=0xFF)
;
sprintf(s,"status=%X\n",status);
sendSerialString(s);
}
The output of the code above:
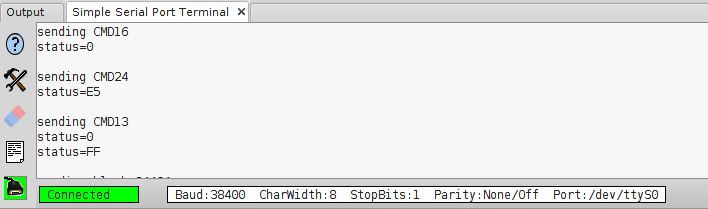
In this case the state byte has 0xE5 value that is 0b11100101 in bit representation. The value means that data was accepted for writing.